On the 16th of May 2023, a Law on Taxation (“New Law”) was promogulated by virtue of Royal Kram No. NS/RKM/0523 on an urgent basis and therefore has come into force from 17th May 2023. The New Law abrogates the previous Taxation Law (“Former Law”) and its Amendment Law which was promulgated by Royal Kram No. NS/RKM/0297/03 dated 24th February 1997 and Royal Kram No. NS/RKM/0303/010, dated 31st March 2003, respectively.
The New Law’s implementation is to centralize all existing tax regulations, reflect the applicable international tax treaties and trends, and ensure that the laws is aligned with the 2021 Law on Investment regarding the tax deduction of expenses, the minimum tax exemption, the domestic VAT on Production Inputs, Non-Resident E-Commerce Value added Tax regime.
This Law contains 20 Chapters and 255 Articles, a significant increase from the Former Law which contained 7 chapters and 155 Articles in which only 9 Articles remain the same under the New Law. These new additional chapters are dealing with several kinds of tax which was previously contains in separate regulatory framework including Specific Tax (Chapter 5), Public Lighting Tax (Chapter 6), Accommodation Tax (Chapter 7), Patent Tax (Chapter 8), Advertising Panel Tax (Chapter 9), Rental of Immovable Property Tax (Chapter 11) and Immovable Property Tax (Chapter 12), Stam Duty (Chapter 13), Capital Gains Tax (Chapter 14), Unused Land Tax (Chapter 15) and Transportation Tax (Chapter 16). These additional Chapters reflect the overarching goal of unifying existing tax laws, international tax agreements, and tax procedures in order to close loopholes and assure consistency.
The followings are some key features of the New Law:
The definitions article, Articles 5 of the New Law, is updated to include more defined terms of “Permanent Establishment” and “Related Party” and introduce a new term concerning “Business Alliances”. These new definitions are made in accordance with the reflection of the applicable international tax treaties and trends.
Additionally, a few types of tax terms are changed under the New Law such as:
The tax regulations of the Kingdom of Cambodia are divided separately making it difficult for the public, taxpayers, and tax officials to track down the entire set of laws and occasionally leaving out certain tax duties. Furthermore, in line of the economic growth, the development of private sector, and the growth of development partners, the New Law is modernized its technical terms and wording, while the content of the of the previous law remains the same, in the original state, including the tax rate. Some terms are intended to be appropriate and consistent with other laws, rules, and regulations. To ensure the convenience, clarity, and advancement to the public, taxpayers, and tax officials, the New Law is contributed with the regulations of all tax types as follows:
Cambodian Sourced Income has been updated to include gains from the sale or transfer of immovable or immovable property or interest properties or interest, services, and the income from business activities of taxpayers thereof, including intangible assets located in Cambodia.
The New Law creates significant developments that the tax authorities can communicate with taxpayers by electronic communication to the existing. The written form of any letter or notification that the tax administration needs to provide to the taxpayer in order to impose an obligation on the taxpayer may now be in electronic form, such as fax and email, and the date of the notification shall be the date on which the message was sent.
The New Law provides the particular importance with respect to such as tax audits which require to the taxpayer responses to submit within a prescribed timeframe. Additionally, the law also gives discretion to the authority to create an incentive scheme for tax officials to fulfill or partially waive penalties and interest on taxpayer for reassessments, to prioritize tax liens over general creditor rights. In addition, the New Law obliges that third parties, such as banks, cooperate with the tax authority to obtain taxpayer information within a set timeframe, otherwise they will face a penalty.
The New Law imposes 04 (Four) new tax crimes which are outlined as the following:
The above offenses are not just subject to a penalty, up to USD 25,000 (twenty-five thousand US dollars), but also potentially to imprisonment, up to 3 years, for those found guilty of the offenses.
Article 225 lists down 13 items of acts, 8 of which are from the Former Law, as obstructing the tax law application.
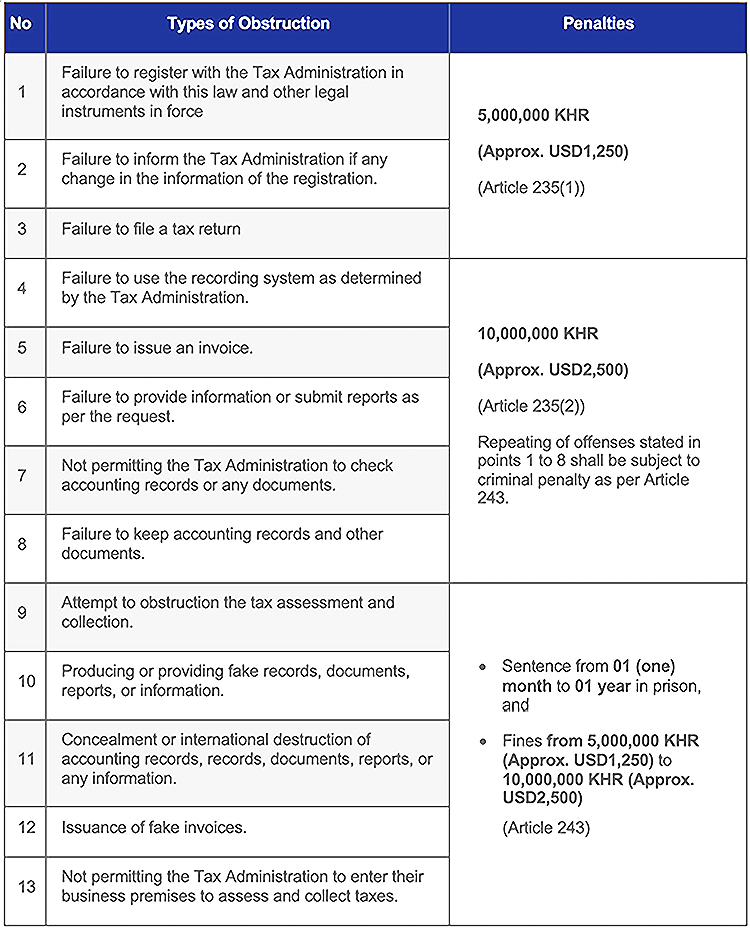
According to the clarification from the General Department of Taxation during its virtual seminar about this law, this New Law does not impose any additional taxes or tax practice that would pressure or confuse the public or entrepreneurs. Instead, it makes it simpler for the taxpayer to be aware of all applicable tax laws and regulations. Unless new Prakas or other legislation might stipulate otherwise, the taxpayers must retain their current tax practices.
Ms. TAN Sambathmarina
Associate
RHTLaw Cambodia
M +(855) 89 780 452
T +(855) 23 886 616
E marina.tan@rhtlawcambodia.com